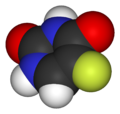
 |
| Fluorouracil Molecule (Color-coded by atom) |
 |
| Dash Model (Heterocyclic Shape) |
Final Dash Model With Polarity
(based on electronegativity table)
Polarity of Bonds: Electronegativity Difference:
N-H: Moderately Covalent .8
C-H: Very Covalent .3
C-N: Very Covalent .5
C-O: Moderately Covalent 1
C-F: Slightly Covalent 1.5
C-C: Completely Covalent 0
The molecule above is a polar molecule.
When reacted with itself the molecule experiences: London Dispersion Forces, Dipole-Dipole Forces, and Hydrogen Bonding.
London Dispersion Forces: A weak and temporary bond due to the uneven distribution of electrons that creates a temporary dipole.
Dipol-Dipol Forces: An electrostatic attraction between the positive end of one molecule and the negative end of another molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding: A special type of dipole-dipole, where Hydrogen makes a temporary bond with the Oxygen or Fluorine in the case of Fluorouracil.

